Photocatalysis using light energy to excite compounds can break and reorganize chemical bonds under mild conditions to initiate a series of photochemical reactions. Compared with conventional thermal transformations, photocatalysis possesses the green and sustainable advantages. It has become a research hotspot in the field of organic synthesis and opened up a new window for carbonyl chemistry due to its unique chemical reactivity. Although a multitude of photocatalytic reactions of carbonyl compounds have been reported, the visible light-induced catalytic asymmetric transformations pose a formidable challenge.
Very recently, Prof. Xiaoming Feng and Prof. Weidi Cao report an enantioselective radical photoaddition to ketones through a Lewis acid-enabled photoredox catalysis, wherein the in situ formed chiral N,Nʹ-dioxide/Sc(III)-ketone complex serves as a temporary photocatalyst to trigger single electron transfer oxidation of silanes for the generation of nucleophilic radical species. The reaction has the advantages of mild conditions, wide substrate applicability and good functional group compatibility. A series of alkyl silanes, including first, secondary and tertiary carbon radical precursors can successfully participate in the reaction, giving a series of chiral tertiary alcohols with moderate to excellent yields and enantioselectivities. It is worth mentioning that this reaction can synthesize histamine antagonist precursor in one step with high enantioselectivity. A variety of mechanism experiments were performed to explore the reaction mechanism. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) detections proved the existence of alkoxy radical and carbon radical, which supported the involvement of radical addition pathway.
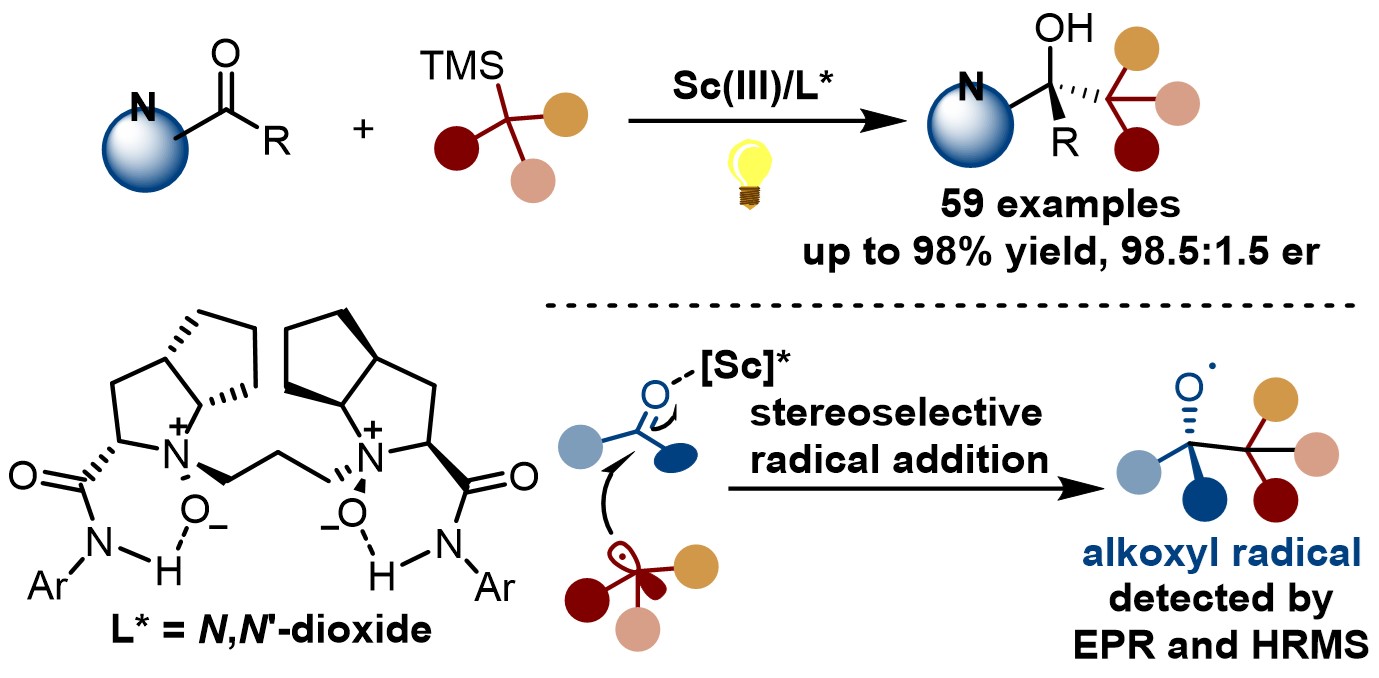
This work is published in Journal of the American Chemical Society:, titled as “Enantioselective Radical Addition to Ketones through Lewis Acid-Enabled Photoredox Catalysis”. Sichuan University is top institute in the address list. Prof. Xiaoming Feng and Prof. Weidi Cao are corresponding authors, and Liuzhen Hou is the first author. This work is financially supported by financial support from the NSFC and the Sichuan Science and Technology Program.
Links to: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/jacs.2c09691
